Constellations of the Month: September – Indus:
We continue September with the last constellation of the month, Indus, “The Indian.”
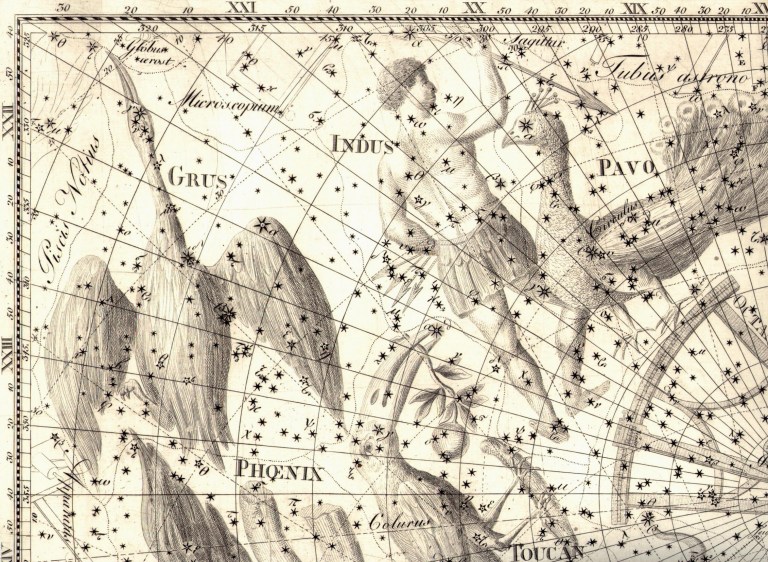
Indus constellation map courtesy of Openverse
Indus, The “Goat” – The Indus constellation is a constellation located in the southern hemisphere, symbolizing the “Indian.” Indus lacks any prominent stars. This constellation symbolizes the Indian, which refers to a native of either Asia or the Americas at the time of its establishment. The constellation was established by the Dutch astronomer Petrus Plancius during the late 16th century and was first illustrated in a star atlas in Johann Bayer’s Uranometria atlas in 1603. Plancius represented Indus as a figure holding arrows in both hands. Indus is considered a relatively faint constellation, with its brightest stars only reaching third magnitude. It encompasses several significant galaxies, including NGC 7049, NGC 7064, NGC 7083, NGC 7090, and IC 5152.

Dust Clouds, variant courtesy of Openverse
Key points regarding Indus:
- Meaning: The term “Indus” translates to “The Indian” in Latin. Indus is part of the Johann Bayer family of constellations, which includes Apus, Chamaeleon, Dorado, Grus, Hydrus, Musca, Pavo, Phoenix, Tucana, and Volans. Indus features two stars that have known planets and does not contain any Messier objects. The brightest star in this constellation is Alpha Indi, also known as The Persian, which has an apparent magnitude of 3.11. There are no meteor showers linked to this constellation. Within Indus, there is one named star, Batsũ̀ (LHS 3844).
- Notable stars: Alpha Indi is a giant star with a spectral type of K0 III-IV, located about 98.3 light years away and has an apparent magnitude of 3.11. It has developed from the main sequence and has two faint red dwarf companions. Alpha Indi has double the mass and twelve times the radius of the Sun and is around a billion years old. Beta Indi is another star, classified as a bright giant with a spectral type of K1II, situated around 600 light years away and has a visual magnitude of 3.658. It also has a visual companion with an apparent magnitude of 12.5. Epsilon Indi is a dwarf star of spectral type K5V, only 11.83 light years from Earth, with two brown dwarf companions discovered in 2003, and is one of the fastest moving visible stars. Theta Indi is a double star situated about 91 light years away, comprising two easily visible components. Rho Indi is an old yellow subgiant with a spectral classification of G2.5IV, located 86.43 light years away, which is nearing the end of its life cycle. It has a planet named Rho Indi b. T Indi is a semi-regular variable red giant star located approximately 1900 light years away with a changing apparent magnitude.
- Other features: NGC 7049 is a galaxy around 100 million light years away, measuring 150,000 light years across, featuring a dust ring and few globular star clusters. Its unique traits result from recent collisions with other galaxies, and a star in its ring belongs to the Milky Way. IC 5152 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Indus, discovered by DeLisle Stewart in 1908. Its membership in the Local Group is uncertain, with a bright foreground star complicating observations. NGC 7090 is a spiral galaxy in Indus, discovered by John Herschel in 1834, and located approximately 30 million light years away. NGC 7083 is a barred spiral galaxy with a magnitude of 12 where a supernova was detected in 2009. NGC 7041, discovered by John Herschel in 1834, is an elliptical galaxy with a magnitude of 11.1. NGC 7064 is another barred spiral galaxy discovered by Herschel. NGC 7029 is a bright elliptical galaxy in Indus, discovered by Herschel in 1834, located about 118.4 million light years away. NGC 7140 is a spiral galaxy found by Herschel in October 1834, situated about 122 million light years away.
- Mythology: There are no legends linked to the constellation. The Indian is typically illustrated with arrows or spears, as if engaged in hunting. The initial representations, such as the one found in Bayer’s Uranometria, suggest that Indus may symbolize a native of Madagascar, as described in the records of Dutch navigators’ inaugural journey to the East Indies. Nevertheless, it remains uncertain whether the constellation genuinely signifies a native of the East Indies, Madagascar, or South Africa, given that the explorers came across various indigenous groups during their expeditions.
- Visibility: Indus is the 49th largest constellation in the sky. It covers an area of 294 square degrees. It is located in the fourth quadrant of the southern hemisphere (SQ4) and is observable at latitudes ranging from +15° to -90°. The constellations that border Indus include Grus, Microscopium, Octans, Pavo, Sagittarius, Telescopium, and Tucana. The name of the constellation, Indus, is pronounced /ˈɪndəs/. In English, it is referred to as the Indian. The genitive form of Indus, which is utilized in the naming of stars, is Indi (pronunciation: /ˈɪndaɪ/). The three-letter abbreviation, which was established by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1922, is Ind.
⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆
Constellations:
| Constellations by Month | ||
| JANUARY [8] | FEBRUARY [7] | MARCH [7] |
| Taurus | Camelopardalis | Ursa Major |
| Orion | Auriga | Cancer |
| Lepus | Gemini | Canis Minor |
| Caelum | Monoceros | Pyxis |
| Reticulum | Canis Major | Vela |
| Dorado | Columba | Carina |
| Pictor | Puppis | Volans |
| Mensa | ||
| APRIL [8] | MAY [7] | JUNE [6] |
| Ursa Major | Canes Venatici | Ursa Minor |
| Leo Minor | Coma Berenices | Boötes |
| Leo | Virgo | Libra |
| Sextans | Corvus | Lupus |
| Crater | Centaurus | Circinus |
| Hydra | Crux | Apus |
| Antlia | Musca | |
| Chamaeleon | ||
| JULY [9] | AUGUST [9] | SEPTEMBER [6] |
| Draco | Lyra | Cygnus |
| Corona Borealis | Vulpecula | Delphinus |
| Hercules | Sagitta | Equuleus |
| Serpens | Aquila | Capricornus |
| Ophiuchus | Scutum | Microscopium |
| Scorpius | Sagittarius | Indus |
| Norma | Corona Australis | |
| Ara | Telescopium | |
| Triangulum Australe | Pavo | |
| OCTOBER [7] | NOVEMBER [8] | DECEMBER [6] |
| Cepheus | Cassiopeia | Perseus |
| Lacerta | Andromeda | Triangulum |
| Pegasus | Pisces | Aries |
| Aquarius | Cetus | Eridanus |
| Piscis Austrinus | Sculptor | Fornax |
| Grus | Phoenix | Horologium |
| Octans | Tucana | |
| Hydrus | ||
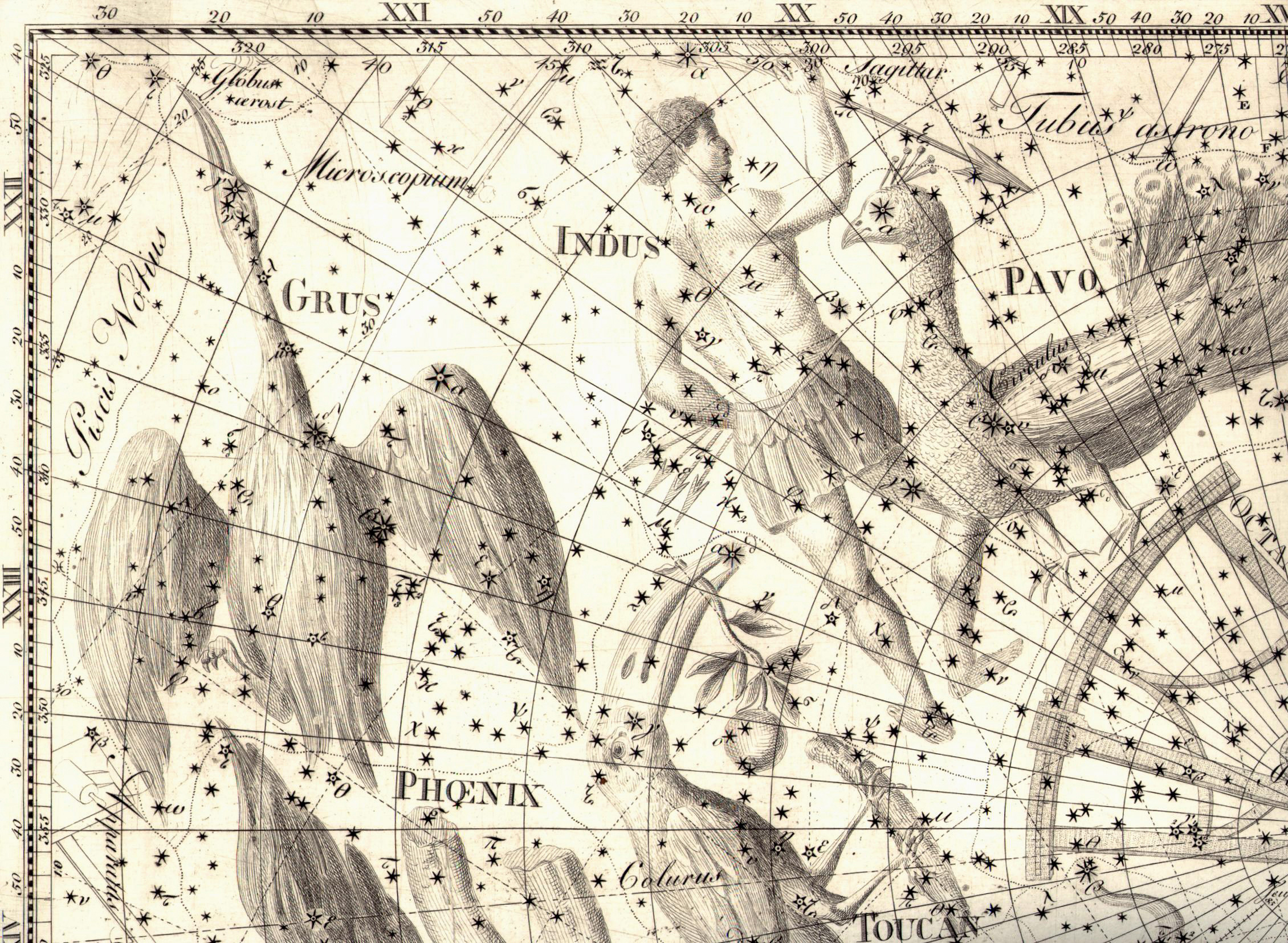
The southern constellation Indus (eso0303d) courtesy of Openverse
Constellations of the Month:
September – Indus
Material may be shared for personal and educational use, Share with family and friends. The material cannot be used in an educational setting whereby a “book fee” is charged in or above tuition costs, and the material here is being used without paying a licensing fee.. AI must file an application for use of such material.
| You May Also Like. . . | |
 NASA 1997 Liftoff Special |
 NASA Mission Patch Party |







Always interesting to see constellations.