Constellations of the Month: April – Crater:
We continue April with the next constellation of the month, Crater, “The Cup.”
Crater constellation map courtesy of Openverse
Crater, “The Cup” – The Crater constellation is a constellation in the southern sky and symbolizes “the cup” in Latin. Crater is faint, with no stars brighter than fourth magnitude and few notable deep sky objects. One galaxy in Crater, the Crater 2 dwarf galaxy, is the fourth largest dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way and was discovered in April 2016.
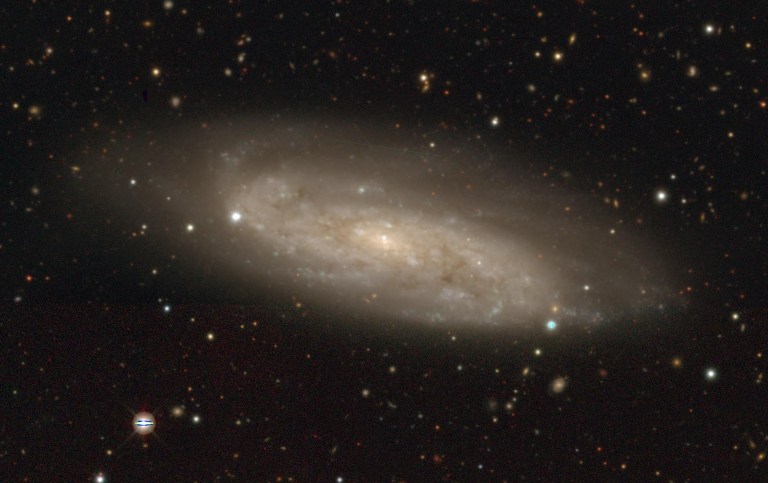

NGC 3511 legacy dr10 courtesy of Openverse
Key points regarding Crater:
- Meaning: The term “Crater” translates to “The Cup.” Crater is part of the Greek constellations and represents the cup of the Greek god Apollo, first catalogued by Ptolemy in the 2nd century.
- Notable stars: Delta Crateris is an orange giant star that is about 196 light years away, classified as K0III, with a brightness of 3.56. It is the brightest star in its constellation and is sometimes known as Labrum, relating to the Holy Grail story. Alkes, or Alpha Crateris, is another orange giant classified as K1, located around 174 light years from Earth, with a visual magnitude of 4.07. It is close to the Galactic center and contains many heavy elements, being 80 times more luminous than the Sun. Its name comes from the Arabic word for “the cup. ” Beta Crateris is a white sub-giant of class A2III, about 266 light years away, with an apparent magnitude of 4.48. It has a traditional name, Al Sharasif, meaning “the ribs” in Arabic.
- Other features: NGC 3887 is an 11th magnitude barred spiral galaxy in Crater, with a diameter of 3.5’. It is about 68 million light years away and was discovered by Sir William Herschel in 1785. NGC 3511 is another spiral galaxy in Crater, seen nearly edge-on, with an apparent magnitude of 11.1, belonging to the Abell 1060 galaxy cluster. It was discovered on December 21, 1786. NGC 3513 is nearby, with an apparent magnitude of 12 and a distance of around 46 million light years. NGC 3981, also found by Herschel in 1785, is a magnitude 12 SBbc type spiral galaxy, 80 million light years away. Crater 2 is a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way, discovered in 2016, and lies about 380,000 light years from the Sun.
- Mythology: In Greek mythology, the Crater constellation represents the cup of the god Apollo. This cup is usually shown as a two-handed chalice. The constellation is linked to the story of Apollo and his sacred bird, either the crow or the raven, represented by the nearby constellation Corvus. In the tale, Apollo needs water for a sacrifice and sends the raven to get it. However, the raven gets distracted by a fig tree and takes days to return. When the raven finally brings back the water, it also brings a water snake as an excuse for the delay. Apollo, realizing the raven’s deception, casts the cup, the snake, and the raven into the sky, cursing the raven to have black feathers and a raspy voice forever.
- Visibility: Crater is the 53th largest constellation, covering 282 square degrees in the southern hemisphere. It is visible between latitudes +65° and -90° and is bordered by Corvus, Hydra, Leo, Sextans, and Virgo. In English, Crater is called the Cup and is pronounced /ˈkreɪtər/. Its genitive form is Crateris, pronounced /krəˈtɪərɪs/. The abbreviation for Crater is Crt. It belongs to the Hercules family of constellations and has three stars with known planets, with Delta Crateris being the brightest. The constellation hosts the Eta Craterids meteor shower and has three named stars: Alkes, Amansinaya, and Hunahpú.
⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆
Constellations:
| Constellations by Month | ||
| JANUARY [8] | FEBRUARY [7] | MARCH [7] |
| Taurus | Camelopardalis | Leo Minor |
| Orion | Auriga | Cancer |
| Lepus | Gemini | Canis Minor |
| Caelum | Monoceros | Pyxis |
| Reticulum | Canis Major | Vela |
| Dorado | Columba | Carina |
| Pictor | Puppis | Volans |
| Mensa | ||
| APRIL [8] | MAY [7] | JUNE [6] |
| Ursa Major | Canes Venatici | Ursa Minor |
| Leo Minor | Coma Berenices | Boötes |
| Leo | Virgo | Libra |
| Sextans | Corvus | Lupus |
| Crater | Centaurus | Circinus |
| Hydra | Crux | Apus |
| Antlia | Musca | |
| Chamaeleon | ||
| JULY [9] | AUGUST [9] | SEPTEMBER [6] |
| Draco | Lyra | Cygnus |
| Corona Borealis | Vulpecula | Delphinus |
| Hercules | Sagitta | Equuleus |
| Serpens | Aquila | Capricornus |
| Ophiuchus | Scutum | Microscopium |
| Scorpius | Sagittarius | Indus |
| Norma | Corona Australis | |
| Ara | Telescopium | |
| Triangulum Australe | Pavo | |
| OCTOBER [7] | NOVEMBER [8] | DECEMBER [6] |
| Cepheus | Cassiopeia | Perseus |
| Lacerta | Andromeda | Triangulum |
| Pegasus | Pisces | Aries |
| Aquarius | Cetus | Eridanus |
| Piscis Austrinus | Sculptor | Fornax |
| Grus | Phoenix | Horologium |
| Octans | Tucana | |
| Hydrus | ||
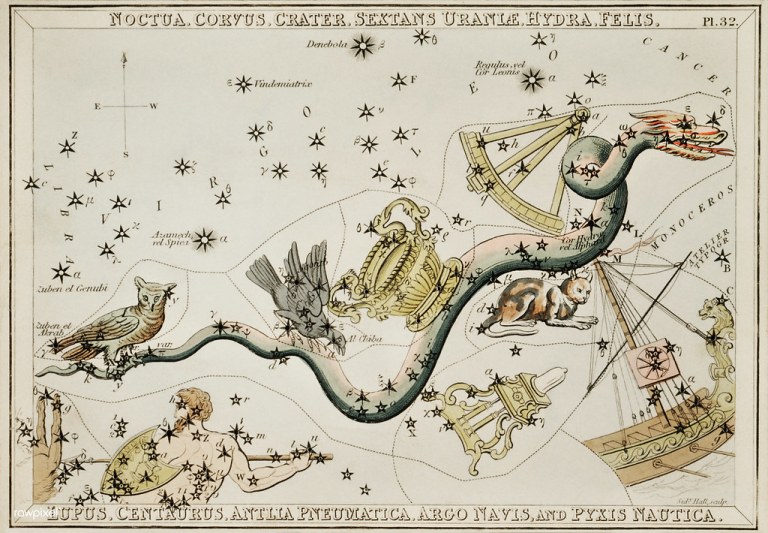
Sidney Hall’s (1831) astronomical chart illustration of the Noctua, Corvus, Crater, Sextans Uraniae, Hydra, Felis, Lupus, Centaurus, Antlia Pneumatica, Argo Navis, and teh Pyxis Nautica. Original from Library of Congress. Digitally enhanced by rawpi courtesy of Openverse
Constellations of the Month:
April – Crater
Material may be shared for personal and educational use, Share with family and friends. The material cannot be used in an educational setting whereby a “book fee” is charged in or above tuition costs, and the material here is being used without paying a licensing fee.. AI must file an application for use of such material.
| You May Also Like. . . | |
 NASA 1997 Liftoff Special |
 NASA Mission Patch Party |







This is very cool to read about! Thank you so much for sharing this chart.
thanks for sharing!
Time to buy a telescope.