Constellations of the Month: April – Leo:
We continue April with the next constellation of the month, Leo, “The Lion.”
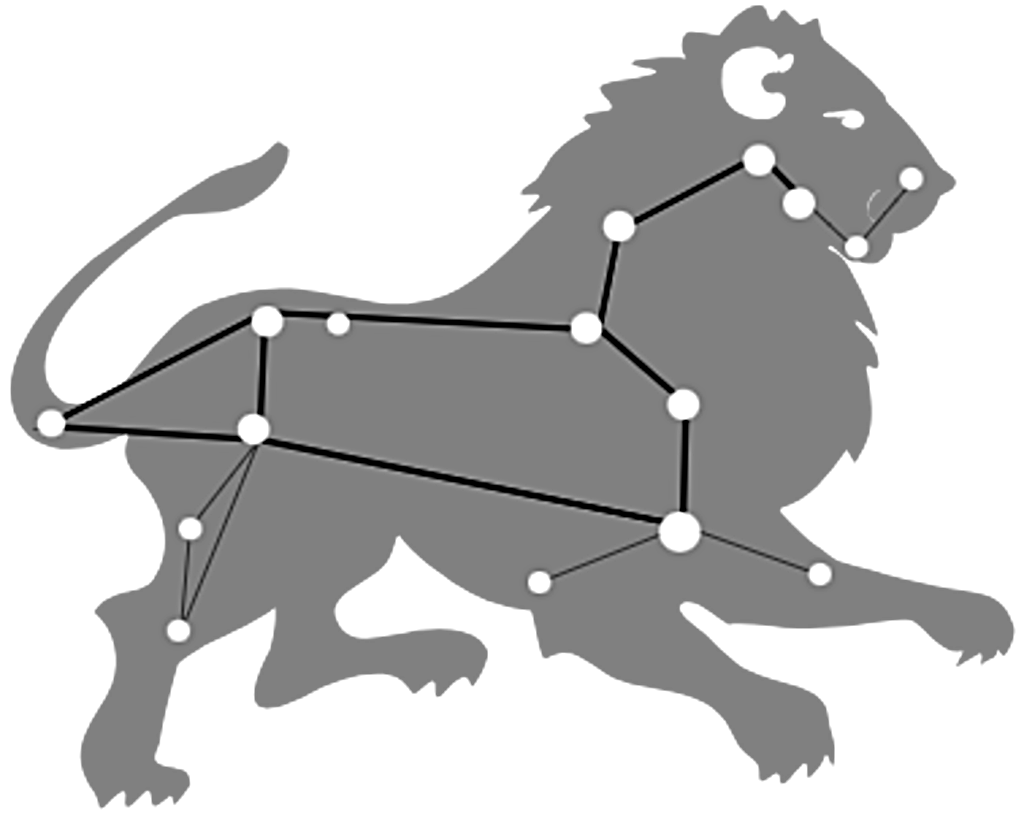
Leo constellation map courtesy of Openverse
Leo, “The Lion” – The Leo constellation is located in the northern hemisphere, and symbolizes “the lion” in Latin. Leo is one of the largest zodiac constellations and represents a lion, linked to the Nemean lion in Greek mythology. Its symbol is ♌. The constellation was catalogued by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the 2nd century. It includes bright stars like Regulus and Denebola, the nearby star Wolf 359, and notable deep sky objects such as galaxies Messier 65, Messier 66, and the Frosty Leo Nebula.

NGC 2903, variant courtesy of Openverse
Key points regarding Leo:
- Meaning: The term “Leo” translates to “The Lion.” Leo is one of the 15 equatorial constellations and has 16 named stars. These stars are Adhafera, Algieba, Alterf, Chertan, Denebola, Dingolay, Formosa, Moriah, Noquisi, Rasalas, Regulus, Sagarmatha, Shaomin, Subra, Yunü, and Zosma. There are two meteor showers linked to Leo: the Leonids, peaking on November 17-18, and the minor January Leonids, peaking between January 1th and 7th.
- Notable stars: Regulus, Alpha Leonis, is the brightest star in the Leo constellation and ranks 22nd in brightness in the sky. It has an apparent magnitude of 1. 35 and is about 77 light years away. Regulus is a four-star system consisting of two pairs of stars. Regulus A includes a blue-white main sequence star and a believed white dwarf companion, orbiting every 40 days. Regulus B and C are dimmer stars with apparent magnitudes of 8. 14 and 13. 5 and share common motion with an orbital period of 2,000 years. Regulus A is a young star, around a few million years old, and has 3. 5 times the Sun’s mass, with a fast rotation period resulting in an oblate shape. Alpha Leonis is close to the ecliptic, making it often obscured by the Moon and occasionally by Mercury and Venus. It is best seen in the evening during late winter and spring, except for a month around August 22. Its name means “little king” in Latin, while the Arabic name means “the heart of the lion. ” Denebola is the second brightest star in Leo, with an apparent magnitude of 2. 113 and a distance of about 35. 9 light years. It is a main sequence star with 75% more mass than the Sun and 12 times more luminous. Denebola shows brightness variations and is classified as a Delta Scuti variable. It is a rapid rotator with a noticeable infrared excess, possibly indicating a dust disk. Denebola is part of the IC 2391 supercluster, which includes other notable stars. Gamma Leonis, also known as Algieba, is a double star system with a giant star and a dimmer companion. Algieba has much greater brightness than the Sun and an orbital period of 500 years. Zosma is another rapid rotator and about 58. 4 light years away. Theta Leonis is a bright white main sequence star approximately 165 light years from Earth. Other notable stars in Leo include Kappa Leonis, Lambda Leonis, and Omicron Leonis, each with unique characteristics and distances from Earth. Eta Leonis is a white supergiant about 2,000 light years away, and Zeta Leonis is a giant star known for its brightness. Mu Leonis and Epsilon Leonis are also part of Leo with significant luminosities. Rho Leonis is a binary system featuring a hot supergiant and was named Shaomin. Iota Leonis is a spectroscopic binary, while Sigma Leonis is a blue-white star. Wolf 359, a faint red dwarf, is very close to the Sun and known for its low energy output. Icarus is a distant blue supergiant discovered through the Hubble Space Telescope. Gliese 436 is another nearby red dwarf with known exoplanets. CW Leonis is a carbon star in a late evolutionary stage, and R Leonis is a Mira variable red giant. Lastly, 31 Leonis is a binary system recognized in Chinese astronomy.
- Other features: Messier 65 is an intermediate spiral galaxy located in Leo, approximately 35 million light years away, with an apparent magnitude of 10. 25. Discovered in 1780 by Charles Messier, it is part of the Leo Triplet group, which includes Messier 66 and NGC 3628. M65 has little dust and gas, mostly old stars, and shows signs of interaction with another object due to its warped disk and recent starburst activity. Messier 66, also an intermediate spiral galaxy, was discovered by Messier in 1780 and is about 36 million light years away with a visual magnitude of 8. 9. It has notable dust lanes and bright star clusters and has interacted with NGC 3628 in the past, resulting in unique features like a high central mass concentration. NGC 3628, an unbarred spiral galaxy discovered by William Herschel in 1784, is about 35 million light years away and has a long tidal tail and a dust band. It forms part of the Leo Triplet as well. Messier 95 is a barred spiral galaxy, approximately 38 million light years distant and has a visual magnitude of 11. 4. Discovered in 1781, it features a central ring-shaped starburst region. A supernova was noted in M95 in 2012. Messier 96 is an intermediate spiral galaxy, about 31 million light years away, known for its supermassive black hole and a supernova discovered in 1998. Messier 105 is an elliptical galaxy, 32 million light years distant, with a central supermassive black hole. The Leo Ring is a cloud of hydrogen and helium discovered in 1983, orbiting two galaxies in the Leo constellation. NGC 3607, NGC 3593, NGC 3384, NGC 3842, NGC 3596, NGC 2903, NGC 3626, and NGC 3357 are additional galaxies in Leo, each with unique features and distances.
- Mythology: Leo is one of the oldest constellations, with evidence suggesting the Mesopotamians recognized it over 5,000 years ago. The Persians called it Shir or Ser, the Babylonians named it UR. GU. LA (“the great lion”), and it had different names in Syrian and Turkish cultures. The Babylonians referred to the star Regulus as “the star that stands at the Lion’s breast” or the King Star. The Greeks linked Leo to the Nemean lion, which Heracles defeated during his first labor. This lion was invincible with impenetrable skin. Heracles couldn’t use arrows against it, so he trapped it in its cave, fought with it, and won. He made a cloak from the lion’s pelt, which protected him and made him look more intimidating. In the constellation, six bright stars form the lion’s head, Regulus marks the heart, Denebola marks the tail’s tip, Algieba is on the neck, and Zosma marks the rear.
- Visibility: Leo is the 12th largest constellation, covering 947 square degrees. It is found in the northern hemisphere (NQ2) and visible between latitudes +90° and -65°. Its neighbors include Cancer, Coma Berenices, Crater, Hydra, Leo Minor, Lynx, Sextans, Ursa Major, and Virgo. The name Leo is pronounced /ˈliːoʊ/ and means Lion in English. The genitive form is Leonis (/liːˈoʊnɪs/), and the IAU abbreviation is Leo. Leo has five Messier objects and 11 stars with known planets. It is part of the Zodiac constellations, which include Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Virgo, Libra, Scorpius, Sagittarius, Capricornus, Aquarius, and Pisces.
⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆⁺‧₊☽◯☾₊‧⁺⋆
Constellations:
| Constellations by Month | ||
| JANUARY [8] | FEBRUARY [7] | MARCH [7] |
| Taurus | Camelopardalis | Leo Minor |
| Orion | Auriga | Cancer |
| Lepus | Gemini | Canis Minor |
| Caelum | Monoceros | Pyxis |
| Reticulum | Canis Major | Vela |
| Dorado | Columba | Carina |
| Pictor | Puppis | Volans |
| Mensa | ||
| APRIL [8] | MAY [7] | JUNE [6] |
| Ursa Major | Canes Venatici | Ursa Minor |
| Leo Minor | Coma Berenices | Boötes |
| Leo | Virgo | Libra |
| Sextans | Corvus | Lupus |
| Crater | Centaurus | Circinus |
| Hydra | Crux | Apus |
| Antlia | Musca | |
| Chamaeleon | ||
| JULY [9] | AUGUST [9] | SEPTEMBER [6] |
| Draco | Lyra | Cygnus |
| Corona Borealis | Vulpecula | Delphinus |
| Hercules | Sagitta | Equuleus |
| Serpens | Aquila | Capricornus |
| Ophiuchus | Scutum | Microscopium |
| Scorpius | Sagittarius | Indus |
| Norma | Corona Australis | |
| Ara | Telescopium | |
| Triangulum Australe | Pavo | |
| OCTOBER [7] | NOVEMBER [8] | DECEMBER [6] |
| Cepheus | Cassiopeia | Perseus |
| Lacerta | Andromeda | Triangulum |
| Pegasus | Pisces | Aries |
| Aquarius | Cetus | Eridanus |
| Piscis Austrinus | Sculptor | Fornax |
| Grus | Phoenix | Horologium |
| Octans | Tucana | |
| Hydrus | ||
Leo Constellation courtesy of Openverse
Constellations of the Month:
April – Leo
Material may be shared for personal and educational use, Share with family and friends. The material cannot be used in an educational setting whereby a “book fee” is charged in or above tuition costs, and the material here is being used without paying a licensing fee.. AI must file an application for use of such material.
| You May Also Like. . . | |
 NASA 1997 Liftoff Special |
 NASA Mission Patch Party |